Serverless Web Application - Example Architecture

Introduction
Building web application backends can be challenging for frontend-focused developers. That is where the serverless web application paradigm comes in handy. Developers can leverage the serverless paradigm to create scalable backend systems easily.
In this post, I will share with you how I have managed to leverage the serverless paradigm & JAMstack principles to build one of my projects.
The basic idea of a serverless architecture is to abstract away the servers and instead focus on consuming resources through APIs. This way the responsibility of maintaining servers moves to the vendors instead of you my dear developer.
As a developer, you can focus on writing the code and solve your unique business problems.
Depending on your use case, this approach can have its shortcomings, there are no silver-bullet solutions here. However, if you are a developer who knows their way around Javascript and your infrastructure requirements are not strict, you will be a lot more productive using the serverless paradigm.
Why serverless
If you are not sure yet, let me share with you some of the good sides of the serverless world.
Cost
You pay for what you use. That means you don't need to pay for idling resources that you utilize occasionally.
Auto-scaling
Your infrastructure has automatically on 100% auto-scaling. No need to worry about setting and maintaining scaling rules.
Smaller team & Maintenance
In a serverless architecture, there are fewer moving parts. This way, you can get quite far with a small dev team. The vendor takes care of security-patches, OS updates, backups, and scalability. So your list of "things to worry about" gets shorter and your team can focus on other important things.
Case study
I decided to follow the serverless architecture for my project Nordgigs.
Technology Stack
Frontend
Serverless & Hosting
Third-party
Architecture
Here is a high-level minimal version of the project architecture to demonstrate how different parts are connected. Keep in mind, this is a simplified version just to demonstrate how a serverless architecture using these tools would work on a high-level.
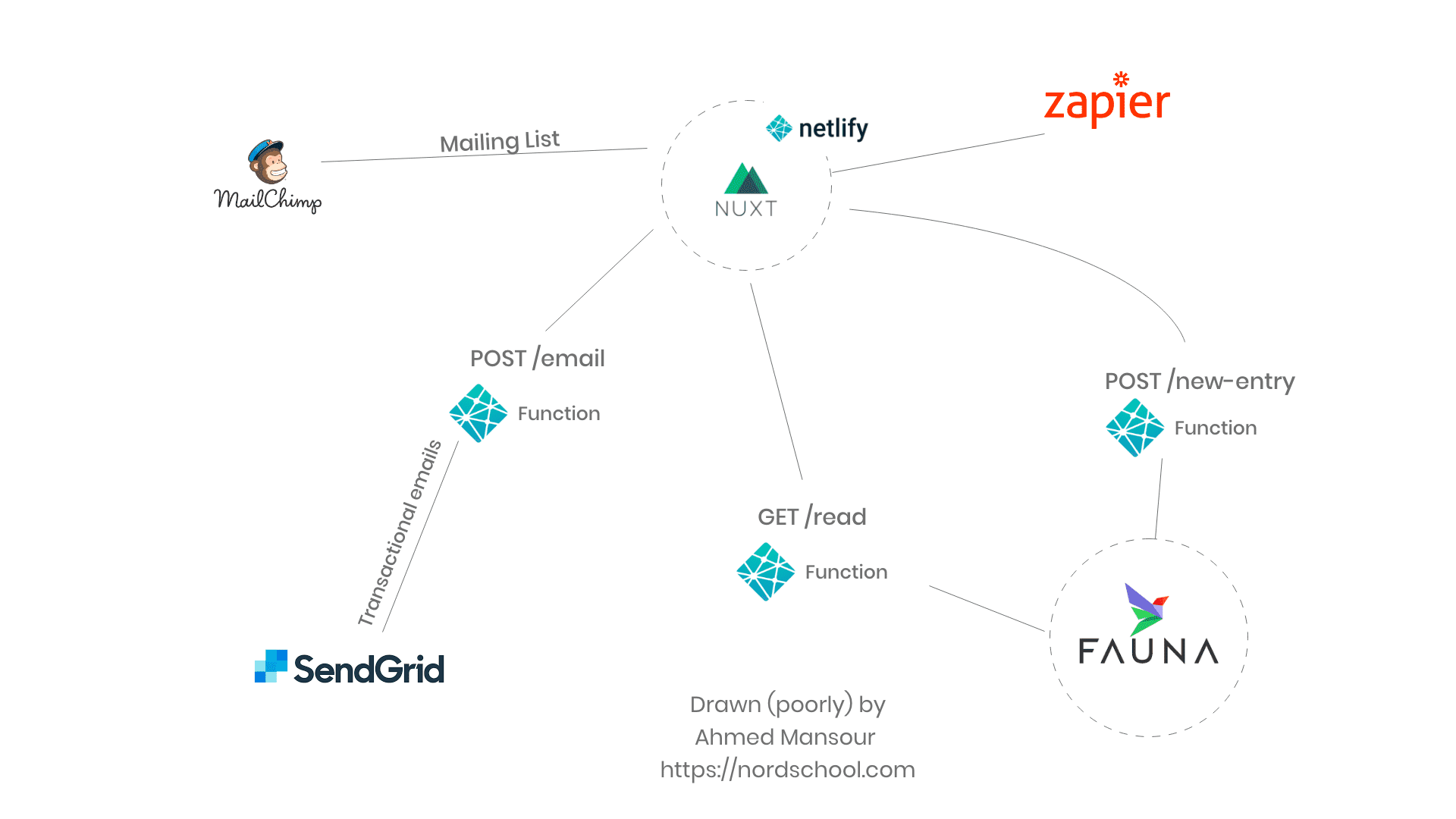
I also followed a JAMstack approach. If you are not sure of what is that, you can find out more about it here.
Netlify & Netlify functions
Netlify serves two purposes in this setup:
- As a hosting platform.
- To easily create & deploy serverless functions.
Out of the box, Netlify integrates with Github, offers CI & a reliable CDN.
Netlify Function is a service that abstracts AWS Lambda's and allows you to easily create full API endpoints per function. They also have a generous free tier that offers 125k requests & 100 hours runtime per month.
I use Netlify since it provides simple basic cloud functionalities so for my use-case it was the obvious choice to be productive as soon as possible.
Vue & Nuxt
I built the frontend using Nuxt & Vue.
I enjoy the simplicity of Vue I tend to choose it in my greenfield projects. As for Nuxt, it makes me productive quickly building Universal Vue apps.
Out of the box, Nuxt makes it easy to create universal apps and offers different on-demand modules such as Vuex & Typescript support.
The JAMstack approach was a good option for my use-case. With the help of Nuxt I can easily create Vue web apps that follow the JAMstack principles.
FaunaDB
I considered other options such as:
- Google's Cloud Store & Firebase
- Amazon's Aurora & DynamoDB
- Azure's Cosmos
- MongoDB Atlas
Since I am not using any of these big cloud providers I thought it might be overkill to introduce one of these cloud providers just for my database. - Keep in mind this is a fairly small project at the moment.
FaunaDB is a serverless cloud database. Some of the things that drew me to try FaunaDB out:
- Big enough free tier for experimenting.
- GraphQL support.
So far my developer experience has been positive and the learning curve has been low.
Mailchimp, Sendgrid & Zapier
Mailchimp is used to manage Nordgigs' mailing list and communicate with the subscribers.
Sendgrid is used to send transactional automated emails to recruiters that add a new project post to Nordgigs' job board.
Zapier is used to automate sending campaigns through Mailchimp, spread the word on social media & other repetitive maintenance tasks.
I am researching options on how to integrate my transaction emails & newsletter campaigns in one tool instead of using two separate tools, will share later on the blog the results I have found.
I am working on producing video tutorials that explain in more detail how you can build such a serverless web app with more code snippets.
If you are interested and would like to hear from me when these tutorials are published, sign up for my newsletter or follow me on twitter.
P.S: If you are interested in freelance projects in Finland, make sure you subscribe to Nordgigs newsletter.
Support us
Enjoyed the article? Share the summary thread on twitter.
